Home » Functional and Sustainable Polymers » Plastic Electronics
Plastic Electronics or Plastronics is a new discipline that includes the integration of electronic components in plastic materials, the use of electrically conductive polymers as well as the development of flexible electronics by printing electronic circuits with conductive inks on polymeric films.
These technologies enable plastic products with integrated electronics to be produced using plastic transformation processes, such as thermoforming and injection or 3D printing. Plastic sensors or tactile parts can also be produced.
In this way, lightweight and flexible components that can be integrated into products with complex geometries can be produced and manufactured on a large scale.
At GAIKER, we are researching the following lines:
Formulation of materials with electronic functionality, resistive and piezoresistive conductors and sensors.

The aim of this project is to increase R&D on materials and processes to ensure that the Basque Country has sufficient knowledge of and capabilities in 3D electronic printing technologies, but also to ensure the sustainability of the materials and end products.
Subsidised by the Basque Government

In the HAPPINESS project, prototypes demonstrating new surfaces with improved human-computer interaction, particularly in the automotive market, were developed through the integration of electronics in the plastic material transformation processes.
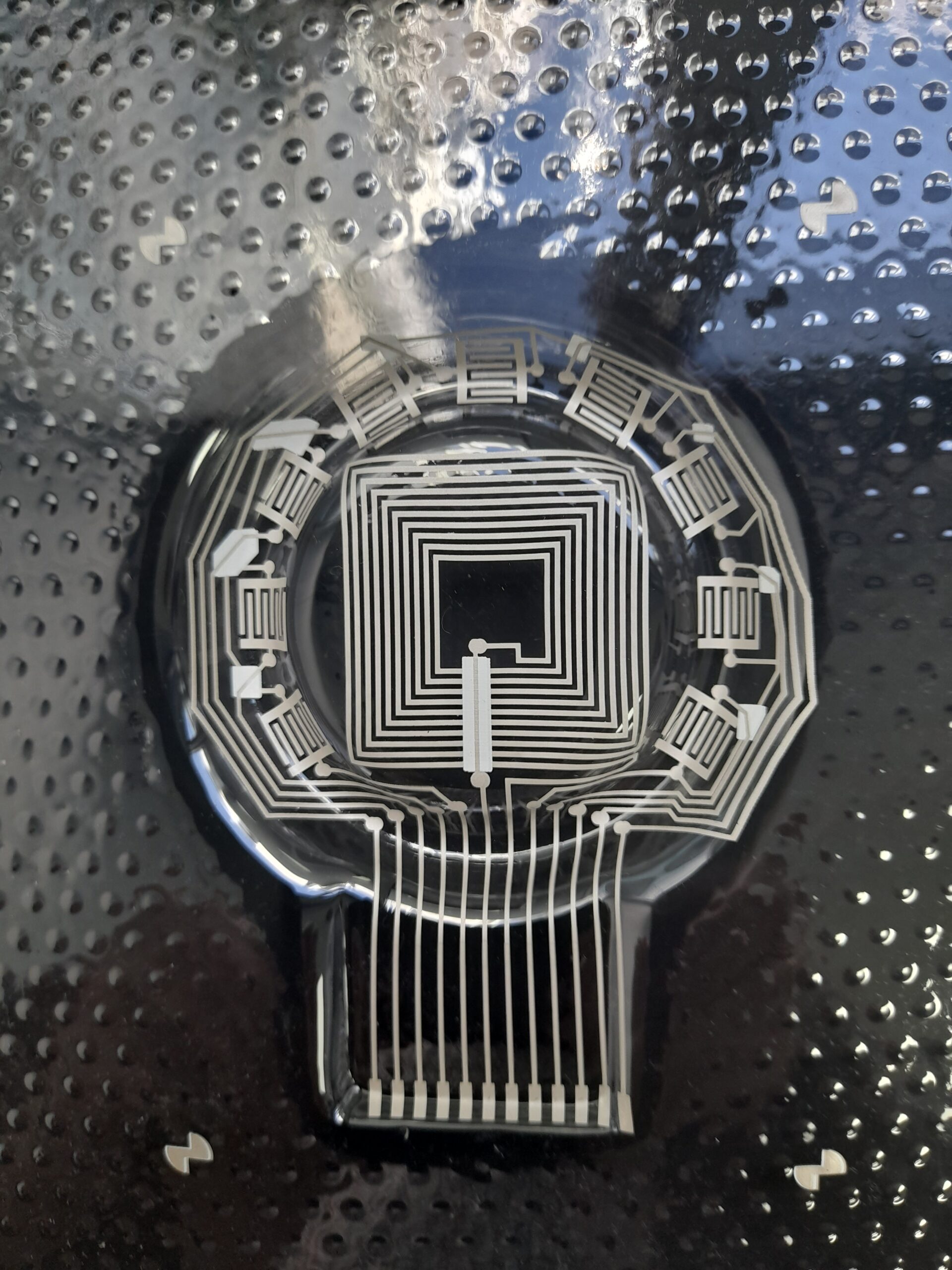
The main aim of this project is to develop new materials and printing and integration processes in order to create true printed electronics that make it possible to produce personalised, functional products in a single manufacturing process. Research is being carried out into 3D printing processes such as fused deposition modelling (FDM) and integration technologies such as in mould electronics (IME), which makes it possible to combine 2D flexible electronics printing with thermoforming and injection moulding to create 3D products with embedded electronics in plastic parts and 3D components.
Subsidised by the Basque Government
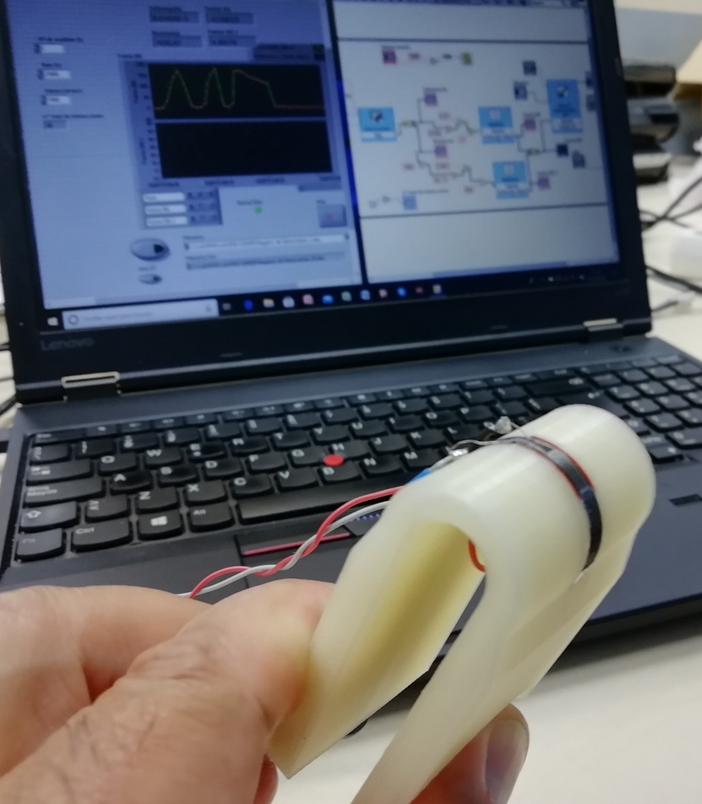

This project focuses on using piezoresistive polymer matrix sensors as a strain sensor to study their ability to be transformed by FDM additive manufacturing processes and the injection moulding process.
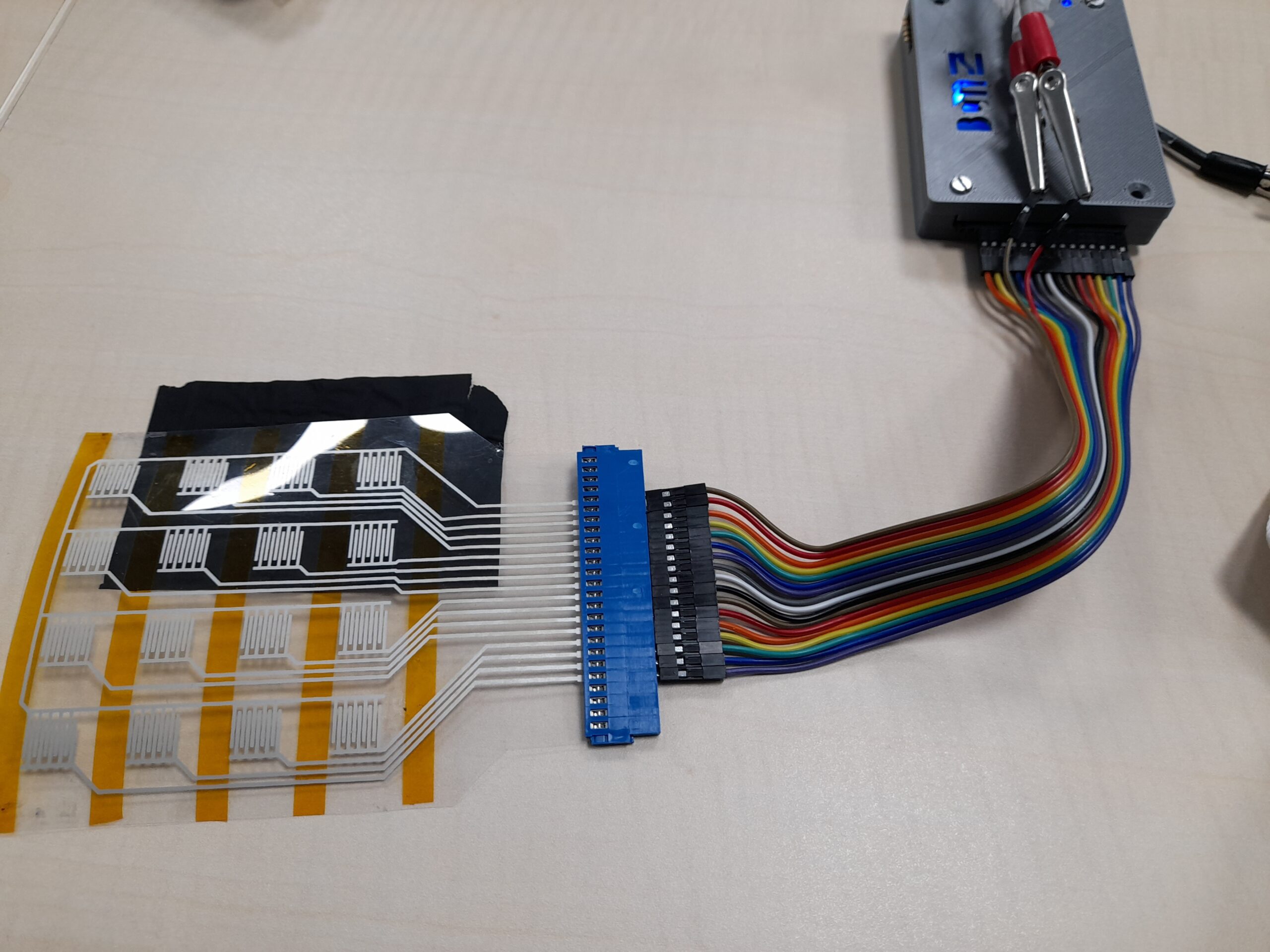
The main aim of the TouchSensor project is to obtain new injection moulded products with touch functionality on a specific area of their surface.

Sustainable Composites & Functional Polymers Market Manager